This tutorial is about how to create a pawn object in the scene. A 'pawn' is a spatial object that can be moved, rotated in the scene. It can be used to represent things that can be manipulated spatially in the scene such as lights or cameras.
To create a pawn, simply use the following command :
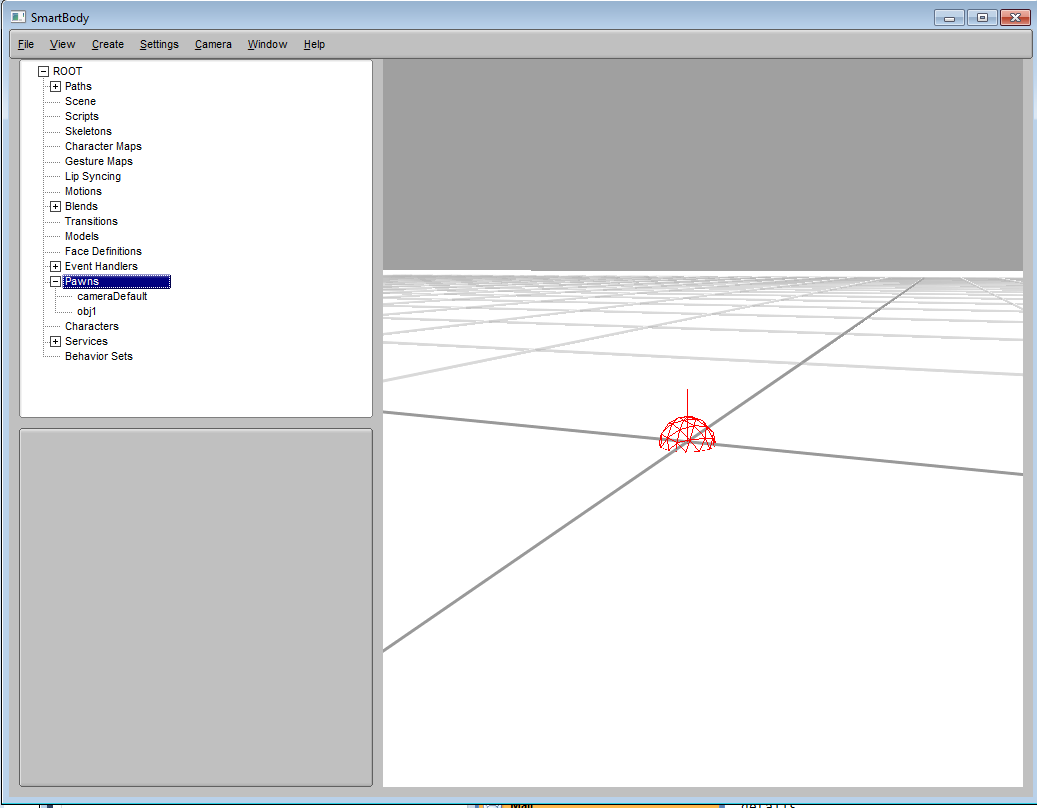
obj = scene.createPawn('obj1')
It will create a pawn object with name 'obj1'. The newly created pawn will appear as a red wireframe ball on the screen.
We can then assign the geometry for this pawn by setting its shape properties :
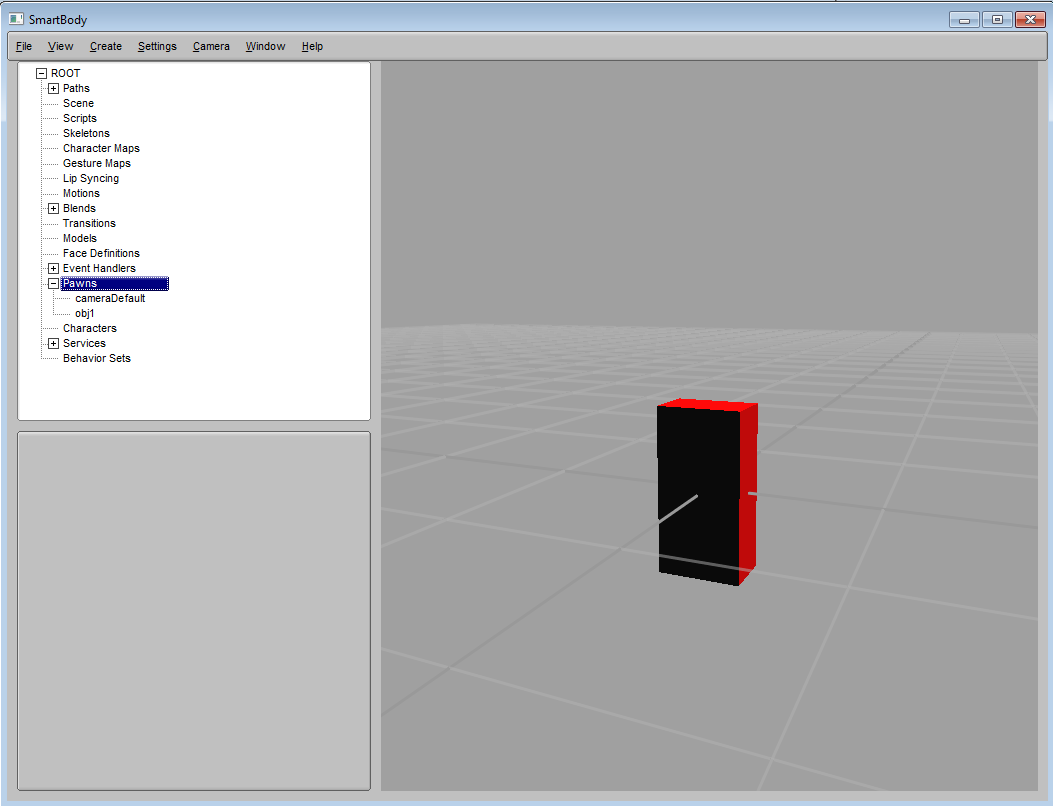
obj.setStringAttribute('collisionShape','box')
obj.setVec3Attribute('collisionShapeScale',5.0,10.0,3.0)
In the above codes, we set the shape to a 'box' and scale the shape size in x,y, and z directions. This will create a rectangular box like the following image (note that the box will penetrate the floor, which can be turned off using View->Show Floor):
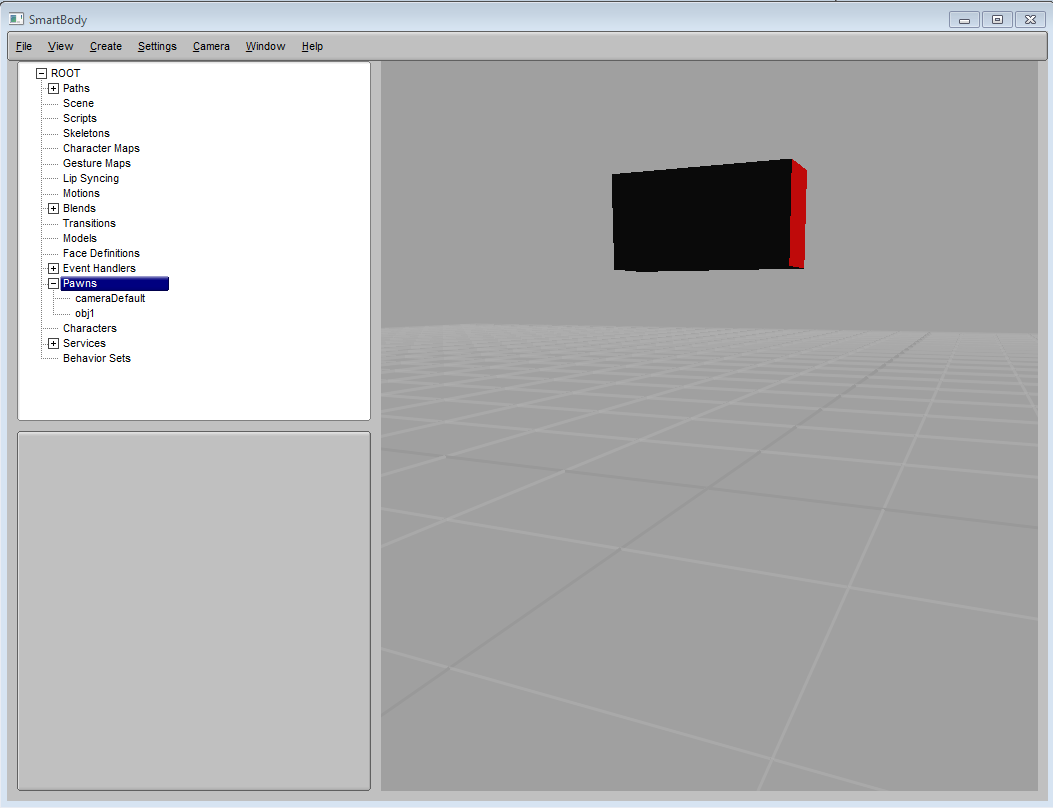
We can also apply further operation on the pawn object to adjust its positions and rotations :
obj.setPosition(SrVec(0,30,0)) obj.setHPR(SrVec(0,0,90))
This will move the object up in Y-axis and rotate it by 90 degrees.
There are more advanced properties such as physics and 3D mesh models that can be applied on a pawn. We will discuss about these in more advanced tutorials.