In this tutorial, we will discuss about setting up a SmartBody character using the assets loaded in the previous tutorial. Load the assets as before, and set the scene scale to 1.0 (meters) instead of the default of .01 (centimeters).
# Add asset paths
assetManager = scene.getAssetManager()
assetManager.addAssetPath('motion', 'ChrBrad')
assetManager.addAssetPath('mesh', 'mesh')
assetManager.addAssetPath('script', 'scripts')
# Load assets based on asset paths
assetManager.loadAssets()
# set the scene scale and reset the camera
scene.setScale(1.0)
scene.getActiveCamera().reset()
Now assign a correct joint map for the loaded skeletons and motions :
scene.run('zebra2-map.py')
zebra2Map = scene.getJointMapManager().getJointMap('zebra2')
bradSkeleton = scene.getSkeleton('ChrBrad.sk')
zebra2Map.applySkeleton(bradSkeleton)
zebra2Map.applyMotionRecurse('ChrBrad')
The above code first run 'zebra2-map.py' to define a joint map for 'zebra2' type skeleton and motions. Then it applies the 'zebra2' joint map on the 'ChrBrad' skeleton and its corresponding motions. This step is necessary to adapt the asset data to be used by SmartBody. Since the naming conventions for joint/bone names may be different between SmartBody and the loaded assets, the joint map acts as a converter to translate the joint names so SmartBody can operate on these assets. For now, let's just assume these are necessary steps before creating a character. More details will be explained in future tutorials and in Section Using Custom Skeletons and Animations.
Once the correct joint map is applied, we can create the character with following commands :
# Set up Brad
brad = scene.createCharacter('ChrBrad', '')
bradSkeleton = scene.createSkeleton('ChrBrad.sk')
brad.setSkeleton(bradSkeleton)
# Set standard controller
brad.createStandardControllers()
The above commands are straightforward. We first create a character with name 'ChrBrad', and then assign a skeleton 'ChrBrad.sk' to him to define the skeleton hierarchy for the character. Then it calls 'createStandardControllers' to create a set of default controllers for the character to enable the capabilities such as gaze, head nods, etc.
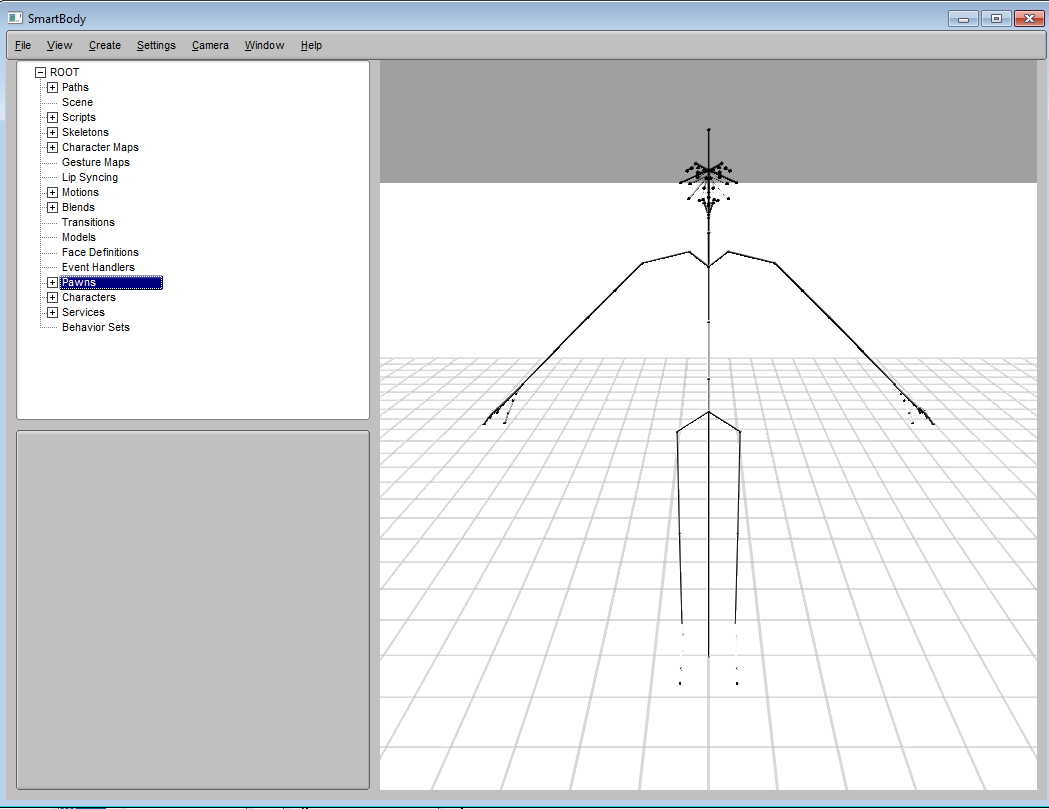
At this point, the character will show up only as skeleton instead of a 3D model like in the following image. This is because we only provides the skeleton information to define the character.
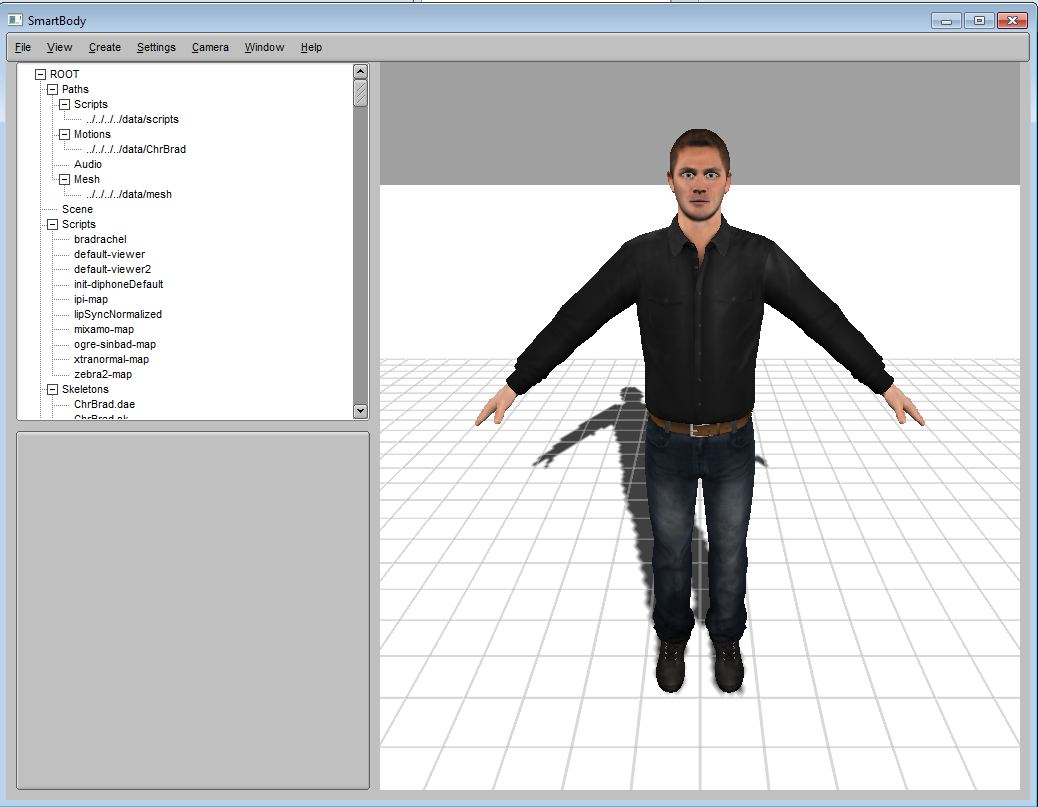
To also load and set the 3D character model, we need to define the character skin mesh for ChrBrad :
brad.setDoubleAttribute('deformableMeshScale', .01)
brad.setStringAttribute('deformableMesh', 'ChrBrad.dae')
# show the character
brad.setStringAttribute('displayType', 'GPUmesh')
Here we first set the mesh scale to be 0.01. This is because the character mesh is in centimeter scale but the 'ChrBrad.sk' skeleton is in meter scale. Therefore we need to rescale the mesh to fit the skeleton. Then we set the 'deformableMesh' attribute to 'ChrBrad'. This will ask the system to search for 'ChrBrad' skin mesh in the search directory, load the files, and then apply the mesh to the character. Once the skin mesh is setup correctly, setting the attribute called 'displayType' will tell the renderer to show the mesh instead of bones. You can also select View->Character->Deformable Geometry from the menu to render all meshes for all characters.
The full setup script for creating the above character is :
print "|--------------------------------------------|"
print "| Starting Tutorial 4 |"
print "|--------------------------------------------|"
print 'media path = ' + scene.getMediaPath()
# Add asset paths
assetManager = scene.getAssetManager()
assetManager.addAssetPath('motion', 'ChrBrad')
assetManager.addAssetPath('mesh', 'mesh')
assetManager.addAssetPath('script', 'scripts')
# Load assets based on asset paths
assetManager.loadAssets()
# set scene scale and reset the camera
scene.setScale(1.0)
scene.getActiveCamera().reset()
# run a Python script file
scene.run('zebra2-map.py')
zebra2Map = scene.getJointMapManager().getJointMap('zebra2')
bradSkeleton = scene.getSkeleton('ChrBrad.sk')
zebra2Map.applySkeleton(bradSkeleton)
zebra2Map.applyMotionRecurse('ChrBrad')
# Set up Brad
brad = scene.createCharacter('ChrBrad', '')
bradSkeleton = scene.createSkeleton('ChrBrad.sk')
brad.setSkeleton(bradSkeleton)
# Set standard controller
brad.createStandardControllers()
# Deformable mesh
brad.setDoubleAttribute('deformableMeshScale', .01)
brad.setStringAttribute('deformableMesh', 'ChrBrad.dae')
# show the character
brad.setStringAttribute('displayType', 'GPUmesh')