SmartBody characters can use gesturing as well as speech to communicate. Gestures are animations associated with an underlying body posture. Gestures differs from playing animations directly in that a BML command for a gesture includes the gesture type, handedness and style. These characteristics are then mapped to the appropriate underlying animation automatically through gesture maps, without the user needing to know which animation is appropriate for the character at that time. For example, using the BML command:
<gesture type="YOU" hand="RIGHT_HAND"/>
would trigger the 'YOU' gesture for a character using the right hand. The gesture map would find the animation associated with a right-handed 'YOU' gesture, determine which posture the character is in, then play that animation. The purpose of the gesture map is to simplify the gesturing commands for the user, since otherwise they would have to know which animation is associated with what posture.
Note that the gesture mapping places the burden of mapping animations to gestures on the frees the simulation user to specify gestures, and places the burden of matching gestures to animation on the simulation designer.
Setting Up a Gesture Map
To create a new gesture map:
mymap = scene.getGestureMapManager().createGestureMap(characterName)
where 'characterName' is the name of the character for which the gesture map will be created. Then to add gestures:
mymap.addGestureMapping(animationName, lexeme, type, hand, style, posture)
where 'animationName' is the name of the animation to be played, 'type' is a variation of the gesture (can be blank), 'lexeme' is the kind of gesture(say, 'POINT', or 'WAVE', or 'YOU' or 'ME', an arbitrary string describing the gesture), 'posture' is the name of the underlying idle pose, and 'hand' is either 'RIGHT_HAND', 'LEFT_HAND', or 'BOTH_HANDS'.
For example, the following will create a gesture map for every character in the scene:
gMapManager = getScene().getGestureMapManager()
numCharacters = scene.getNumCharacters()
charNames = scene.getCharacterNames()
for i in range(0, numCharacters):
gMap = gMapManager.createGestureMap(charNames[i])
gMap.addGestureMapping("HandsAtSide_Arms_Sweep", "SWEEP", "", "BOTH_HANDS", "", "HandsAtSide_Motex")
gMap.addGestureMapping("HandsAtSide_RArm_GestureYou", "YOU", "", "RIGHT_HAND", "", "HandsAtSide_Motex")
gMap.addGestureMapping("LHandOnHip_Arms_GestureWhy", "WHY", "", "BOTH_HANDS", "", "LHandOnHip_Motex")
gMap.addGestureMapping("LHandOnHip_RArm_GestureOffer", "OFFER", "", "RIGHT_HAND", "", "LHandOnHip_Motex")
gMap.addGestureMapping("LHandOnHip_RArm_SweepRight", "SWEEP", "", "RIGHT_HAND", "", "LHandOnHip_Motex")
gMap.addGestureMapping("LHandOnHip_RArm_SweepRight", "YOU", "", "RIGHT_HAND", "", "ChrUtah_Idle003")
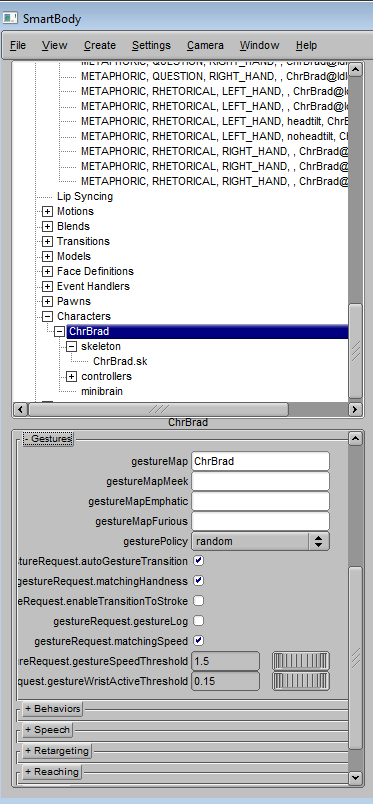
Once gesture map is setup, it can be assigned to each character by setting following attribute.
gestureMap: gesture map used under neutral emotion state, also the default one.
gestureMapEmphatic: gesture map used under angry emotion state, if not set, will use gestureMap instead.
gestureMapMeek: gesture map used under sad emotion state, if not set, will use gestureMap instead.
Gesture Motion
Sync Points
Gesture motion sync points are important for gesture holding and transition. When artist creates the gesture motion, it's preferred artist understand how these sync points are used and mark them correctly. For more detailed information, please go to BML standard 1.0 webpage.
http://www.mindmakers.org/projects/bml-1-0/wiki#Timing-and-synchronisation
start: start time.
ready: ready time. Gesture will get to the pose where it starts the stroke. (Also when doing pre stroke gesture hold, the inserted motion frames are referring to ready frame).
stroke_start: stroke start time. Gesture sometimes has a pre-stroke hold time period defined by time gap of ready and stroke_start.
stroke: stroke time. This is where gesture hit the emphasis point overshoot. If gesture is transition from one holding position directly to another holding position, (stroke - stroke_start) will be the transition duration. More detailed can be found in BML behaviors' gesture section.
stroke_stop: stroke end time. This is where the gesture hit the emphasis point and come back from the overshoot, if a gesture emphasis point doesn't have overshoot, then stroke is the same with stroke_stop. (Also when doing post stroke gesture hold, the inserted motion frames are referring to the stroke_stop frame).
relax: relax time. This is when gesture starts to go back to rest pose. The time gap between stroke_stop and relax defined a post-stroke holding period.
stop: end time.
Perlin Noise
Artist can add perlin noise to specific joints at given frequency and scale during gesture holding period by adding extra meta data information to the end of .skm motion files. Following are examples:
noise_joints: "r_shoulder r_elbow l_shoulder l_elbow" noise_scale: 0.05 noise_frequency: 0.015
Gesture Co-articulation and Pruning
Gestures can be blended in at anytime indicated by BML, but under a lot of circumstances, simply blending over-generated gesture animations will look unnatural. Co-articulation is important for creating human like gesture behaviors including holding gestures, transition from one gesture's stroke end to another gesture's stroke start etc. Gesture pruning is also key element in filtering out gestures that's not fit within time constrain, e.g. blend time too short for a huge wrist spatial transition.
Several attributes will affect the co-articulation and pruning.
gesturePolicy: random or first. If set to random, gesture animation will randomly be picked from the pool, otherwise always pick the first one.
gestureRequest.autoGestureTransition: enable gesture co-articulation and pruning, otherwise will be simple blending.
gestureRequest.enableTransitionToStroke: ideally co-articulation ensures transition from one gesture's stroke end to another gesture's stroke start, because the meaning of gesture is contained from stroke start to stroke end. However, if time span for transition is real short, this attribute allows to lose the constrain by blending from stroke end to stroke directly. Trade off is the second gesture will lose the meaning from stroke start to stroke.
gestureRequest.gestureLog: enable log
gestureRequest.gestureSpeedThreshold: default value is 1.5. If gesture's wrist joint transition speed exceeds this threshold, it will be pruned.
gestureRequest.matchingSpeed: this attribute will ensure gesture transition speed will match the speed of next gesture's stroke phase. If transition speed is smaller than next gesture's stroke speed, elongate the first gesture's holding period. If it's larger, than check if transition speed exceeds gestureSpeedThreshold.
gestureRequest.matchingHandness: if this toggle is on, gesture animation picked will take into consideration previous co-articulated gesture animation's handness and try to match it.